Food and Nutrition Applications
To help the agricultural industry flourish in its efforts to maintain fertile land, grow crops and raise healthy livestock, Chevron Phillips Chemical produces agrochemical intermediates such as Dimethyl Disulfide.
Dimethyl Disulfide is also used as a flavor and fragrance intermediate, which enriches the aroma and flavor of certain consumer products.
Refinery Applications
Dimethyl Disulfide (DMDS) is a sulfiding agent, which is used along with a reducing agent such as hydrogen, to transform metal oxide species to a metallic sulfide crystalline phase in situ for hydrotreating catalysts. For in situ sulfiding, the reaction is performed inside the process unit for complete control and to achieve maximum catalyst activity and safe handling.
DMDS can also be used as a passivation agent to reduce the layer of coke that forms within furnaces and improve the run length, yield and life of furnaces.
Advantages
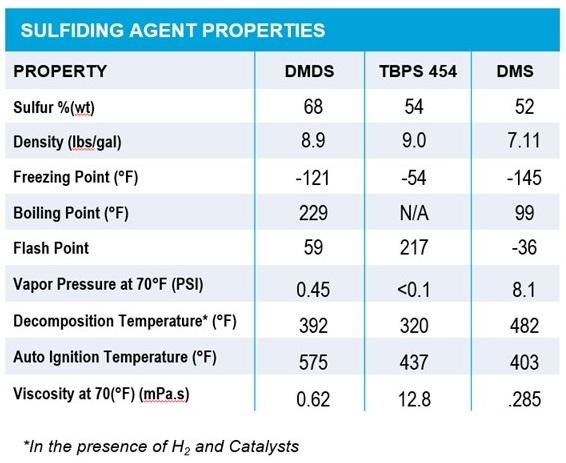
Compared to other sulfiding agents, DMDS has the highest sulfur content, which reduces the amount of product required for converting oxides to active metal sulfides. Thermally stable with low viscosity, DMDS is suitable for gas- or liquid-phase injection. It begins to decompose to H2S at low temperatures, so the risks of reducing the metal oxides prior to sulfiding are eliminated. In addition, DMDS also decomposes in two steps, further minimizing the risk of temperature excursions during sulfiding.
Packaging
DMDS is available in bulk (railcars, tank trucks and ISO containers) or packaged containers including 250 gallon returnable steel totes, 57 gallon returnable steel cylinders or 54 gallon drums.
Safety and Handling
Due to its low vapor pressure, DMDS is a safe product to handle at high ambient temperatures. However, it also has a low flash point and should be handled as a flammable material—stored under inert conditions and away from potential ignition sources. DMDS is a dermal, oral and toxic inhalation material, as well as a marine pollutant. It also may have a slightly unpleasant odor. DMDS generates methane during the sulfiding operation, which if not handled properly, may require purging and undesired SOx emissions. DMDS is not soluble with water, but will solubilize in both amines and ketones. DMDS is compatible with both carbon and stainless steel as long as excess water is not present.
Brass and copper connections are not recommended. Gaskets should be Teflon since DMDS tends to attack rubber and nitrile elastomers. Household bleach (not pure bleach) or Liquid Alive® bacteria is suggested for any necessary clean up. Please reference the Material Safety Data Sheet for additional handling and safety recommendations. The PHMSA mandates that any personnel governed by the USDOT who handle DMDS must be in compliance with the safety requirements stipulated under 49 CFR Parts 177.834.
Performance Data
Perfumed DMDS
Methyl Mercaptan and Dimethyl Sulfide are the two impurities that cause odor in DMDS. Both of these impurities are typically <100 ppm in Chevron Phillips Chemical’s DMDS. A high purity DMDS eliminates the need to add perfume to mask the odor of the product.
Application Guidelines
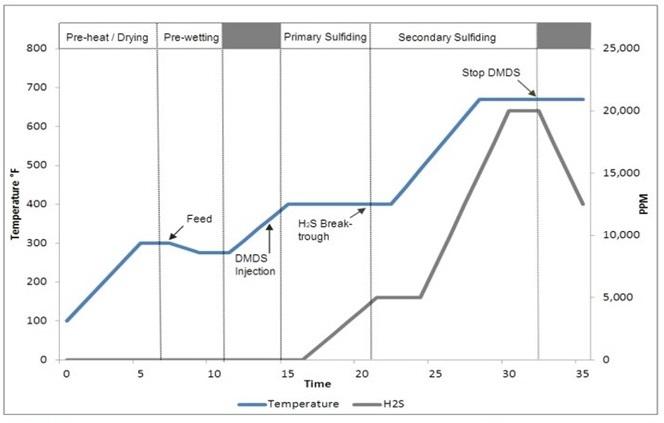
For in situ sulfiding of hydrotreating catalysts, the catalysts will typically be dried and then wetted with feed material at 300°F or below. DMDS injection begins as the temperature approaches 400°F, with the reactor held in a range of 400–420°F until H2S breakthrough occurs.
Breakthrough is indicated when the H2S level of the recycle gas exceeds 5,000 ppm. The reactor temperature can then be raised to the secondary sulfiding plateau, which is typically in the range of 620–670°F. The temperature will be held at this level for at least 4 hours until the sulfiding process is complete. A secondary H2S breakthrough may occur at this point, with H2S levels rapidly exceeding 20,000 ppm. See figure below.
Typical Feed Sulfiding Procedure
For reformer units, a small amount of DMDS is continuously injected, generally about one gallon per day, directly into the feedstock. The DMDS will convert to H2S, which will mitigate the creation of coke.
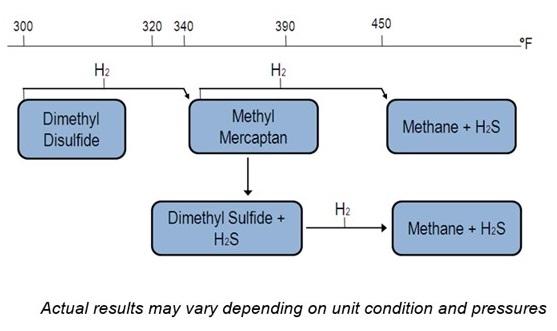
Decomposition of DMDS in the Presence of a Catalyst